An Ink Tank Printer is a modern printing solution created to solve one of the most common problems faced by everyday users: expensive ink replacements. Instead of relying on small, disposable cartridges, this printer type uses large refillable reservoirs that can produce thousands of pages before requiring more ink. This design makes it especially appealing for people who print frequently and want predictable long-term costs.
In this year, the relevance of this printing technology continues to grow. The cost of consumables has increased across many brands, while printing needs have expanded due to remote work, online learning, and home-based businesses. Many households now rely on printers not just occasionally, but as a daily productivity tool. As a result, users are actively searching for printing systems that balance affordability, reliability, and convenience.
Another important factor driving interest is environmental awareness. Traditional cartridge systems generate significant plastic waste, as empty cartridges are often discarded after limited use. Refillable ink systems reduce this waste by allowing users to top up ink directly, cutting down on packaging and transportation emissions. For consumers who care about sustainability, this approach offers a more responsible way to print.
Today’s refillable printers are also far more user-friendly than earlier generations. Manufacturers have refined ink flow control, improved refill mechanisms, and added features that help users monitor ink levels easily. These improvements have helped shift public perception, turning ink tank–based printers from a niche option into a mainstream choice.
This article explains what this printer technology is, how it works, and why it has become increasingly popular. You will learn about its core characteristics, how it compares to cartridge-based models, and the benefits and drawbacks you should consider. By the end, you’ll be able to decide whether this type of printer aligns with your printing habits, budget, and long-term needs.
What Is an Ink Tank Printer?
An Ink Tank Printer is an inkjet printer that stores ink in large, built-in tanks instead of using small, replaceable cartridges. These tanks are refilled using bottled ink and supply a continuous flow of ink to the printhead. The main purpose of this system is to support high-volume printing while keeping the cost per page as low as possible.
Although the printing process itself is similar to that of a standard inkjet—spraying liquid ink onto paper—the difference lies in ink storage and usage efficiency. Cartridge printers depend on compact ink units that often run out quickly, especially when printing documents in bulk. Refillable tank systems, by contrast, are designed to last much longer between refills, making them better suited for frequent use.
When comparing ink tank vs cartridge printers, the trade-off is clear. Cartridge models usually have a lower purchase price and work well for occasional printing. Refillable systems, however, focus on long-term savings. While the initial investment may be higher, users typically spend far less on ink over time, especially if they print hundreds or thousands of pages per month.
As CHOICE tech expert Peter Zaluzny explains:
“Printers can be quite specialised these days, from cheaper models aimed at only occasional use, to ink-tank (not cartridge) models designed for high output at low cost per page.”
This distinction highlights why refillable ink systems are built specifically for volume and efficiency rather than light, infrequent tasks.
Another practical advantage is visibility and control. Many models feature transparent or semi-transparent tanks, allowing users to check ink levels at a glance. This reduces the risk of unexpected ink shortages and helps users plan refills more efficiently.
History & Evolution Ink Tank Printer?
Refillable ink printers gained widespread attention in the early 2010s, largely due to Epson’s EcoTank lineup. At the time, the idea of replacing cartridges with bottled ink challenged long-standing industry practices. The concept quickly resonated with users who were frustrated by frequent cartridge replacements and unpredictable costs.
Seeing strong market adoption, other major manufacturers soon introduced their own versions, including Canon MegaTank and HP Smart Tank models. Each new generation improved ease of use, ink stability, and printhead reliability. Early concerns about spills or maintenance were gradually addressed through better bottle designs and guided refill systems.
Today, this printer category is firmly established across home, education, and small-business environments. With lower running costs, improved reliability, and growing demand for sustainable printing, ink tank–based printers have become a core option for users who value efficiency and long-term value.
How Ink Tank Printers Work
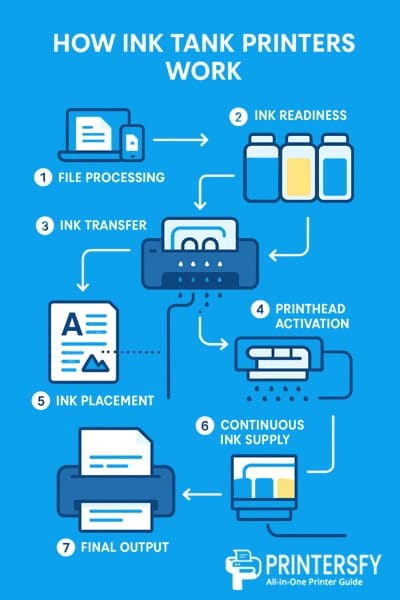
Knowing what an ink tank–based printer is only gives you the basic idea. To understand why this technology is known for lower running costs and stable print results, you also need to see how it actually works in practice.
From the way ink is stored in refillable tanks to how tiny droplets are placed onto the paper, every step is built with efficiency in mind.
Step Process Stage What Happens 1 File Processing A digital document or image is sent from a computer or mobile device to the printer, where it is converted into printable data. 2 Ink Readiness Ink stored in large refillable tanks is kept at a stable level, ready for continuous delivery without pressure loss. 3 Ink Transfer Ink flows through narrow tubing from the tanks to the printhead in a controlled and consistent manner. 4 Printhead Activation The printhead releases microscopic ink droplets using thermal or piezoelectric technology, following precise instructions. 5 Ink Placement Ink droplets are applied onto paper line by line, forming text or images with consistent color density. 6 Continuous Supply The refillable system maintains steady ink flow throughout the print job, avoiding interruptions common with low cartridges. 7 Final Output The printed page exits the printer, while remaining ink stays stored in the tanks for future jobs.
Core Technology Explained
At the heart of an Ink Tank Printer is a refillable ink storage system designed to deliver ink continuously to the printhead. Instead of using sealed cartridges, this technology relies on large ink reservoirs that are filled with bottled ink. These reservoirs can store a significantly higher volume of ink, allowing users to print thousands of pages before needing a refill.
This design is closely related to what is known as a continuous ink supply system (CISS). According to general printing technology references, a continuous ink system feeds ink directly from external or built-in tanks to the printhead through small tubes, ensuring a steady and controlled ink flow. In practical terms, this means less interruption, fewer consumable replacements, and more consistent printing performance.
Compared to cartridge-based systems, refillable ink systems are far more efficient for frequent printing. Cartridge printers rely on small ink chambers that empty quickly, while tank-based designs prioritize volume and longevity. As a result, an Ink Tank Printer is optimized for users who need predictable output and lower long-term operating costs rather than convenience for occasional prints.
Ink Delivery System Components
The ink delivery system in this type of printer consists of several key components working together.
First are the ink tanks, which are usually built into the printer body and often designed with transparent or semi-transparent walls. This visibility allows users to monitor ink levels easily and refill only when necessary.
Next is the tubing system, which connects the tanks to the printhead. These narrow tubes regulate ink flow using gravity or controlled pressure, ensuring the right amount of ink reaches the printhead at all times. This controlled delivery is critical to maintaining print quality and preventing leaks or air bubbles.
Finally, the printhead mechanism applies the ink to paper. Whether thermal or piezoelectric, the printhead sprays microscopic droplets of ink in precise patterns. Because the ink supply is continuous, the system avoids the pressure fluctuations commonly associated with low or nearly empty cartridges, resulting in more stable output over long print runs.
Step-by-Step: How Printing Happens
The printing process begins when a digital file is sent from a computer or mobile device to the printer. The printer’s processor converts this file into printable data, determining color placement, ink density, and print resolution.
Ink is then drawn from the tanks through the tubing and delivered to the printhead. The printhead applies the ink to the paper line by line, creating text or images with consistent saturation. What makes this process efficient is the absence of cartridge limitations—there is no need to pause printing due to low ink pressure or cartridge replacement.
This efficiency is a major reason why an Ink Tank Printer performs well in high-volume environments. Continuous ink availability reduces downtime, while large reservoirs minimize user intervention.
Ink Tank vs Cartridge Printer: Technical Comparison
| Feature | Ink Tank Printer | Cartridge Printer |
|---|---|---|
| Ink Supply | Large refillable tanks | Sealed cartridges |
| Cost per page | Very low (ideal for bulk printing) | Higher, especially for color |
| Waste | Minimal plastic waste | Frequent cartridge disposal |
| Printhead | Often integrated or long-life | Sometimes built into cartridge |
| Ideal for | High-volume printing | Occasional or light use |
Key Characteristics of Ink Tank Printers
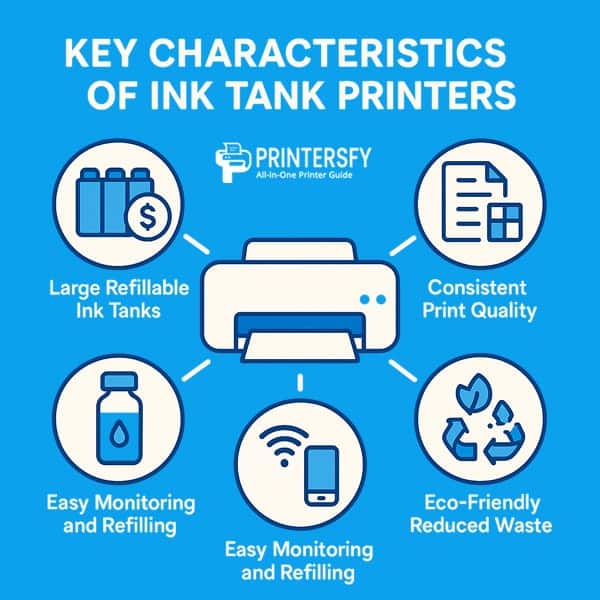
To see what truly sets it apart from traditional models, it helps to look at the key characteristics that define its everyday performance, cost efficiency, and overall user experience.
Large Ink Capacity and Lower Cost per Page
One of the most noticeable characteristics of an Ink Tank Printer is its large ink capacity. Instead of relying on small cartridges, these printers use refillable tanks that can last for thousands of pages on a single refill. This dramatically reduces the cost per page, especially for users who print regularly.
This advantage makes refillable printers particularly suitable for:
- Students with frequent assignments
- Teachers and educators
- Small offices with daily document printing
- Home users who want predictable printing expenses
Consistent Print Quality Across Multiple Uses
Modern refillable printing systems are designed to deliver reliable output over long print runs. Text appears sharp and well-defined, while colors remain accurate and balanced across documents and images.
Key quality benefits include:
- Clear text for reports and schoolwork
- Stable color reproduction for graphics
- Improved ink formulations for smoother output
Advances in printhead technology have helped narrow the quality gap that once existed between tank-based and cartridge printers, making refillable systems suitable even for occasional photo printing.
Eco-Friendly and Reduced Waste
Sustainability is another important feature. By minimizing the need for disposable cartridges, these printers significantly reduce plastic waste and excess packaging.
Environmental benefits include:
- Fewer cartridges ending up in landfills
- Reduced packaging materials
- Lower transportation impact due to bulk ink refills
This makes ink tank–based printers an attractive option for users who want a more environmentally responsible printing solution.
Easy Ink Level Monitoring and Refilling
User convenience is enhanced through visible ink tanks, which allow users to check ink levels at a glance. This removes the guesswork often associated with cartridge printers.
Practical advantages include:
- Instant awareness of remaining ink
- Fewer unexpected print interruptions
- Guided, spill-resistant refill systems
Refilling is typically simple and clean, even for first-time users.
Modern Connectivity and Smart Features
Most current models are equipped with features that support modern workflows, ensuring smooth integration into both home and office environments.
Common features include:
- Wi-Fi and wireless printing
- Mobile printing from smartphones and tablets
- Cloud printing support for remote access
Together, these characteristics allow an Ink Tank Printer to combine efficiency, usability, and modern convenience in a single printing solution.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Ink Tank Printers
Like any printing solution, an Ink Tank Printer offers clear strengths, but it also comes with trade-offs that may or may not suit every user.
Benefits of Ink Tank Printers
Lower Running Costs
One of the biggest advantages of an Ink Tank Printer is its extremely low running cost. Because ink is stored in large refillable tanks, users can print thousands of pages before needing a refill. This dramatically reduces the cost per page compared to cartridge-based printers.
Key benefits include:
- Significantly cheaper ink refills
- Fewer interruptions caused by empty cartridges
- Predictable long-term printing expenses
For users focused on high-volume printing savings, this is often the main reason to choose an Ink Tank Printer.
High Print Volume Capability
Designed for frequent use, an Ink Tank Printer can handle large print jobs without performance drops. This makes it suitable for environments where printing is a daily task rather than an occasional one.
Ideal scenarios include:
- School assignments and study materials
- Office reports and invoices
- Bulk document printing
Unlike cartridge models, these printers maintain consistent output even during long print runs.
Better Long-Term Return on Investment
Although the initial purchase price may be higher, an Ink Tank Printer usually delivers better long-term value. Over time, savings on ink costs often outweigh the higher upfront investment.
From a cost perspective:
- Initial cost is recovered through cheaper refills
- Total ownership cost remains lower after extended use
- Fewer consumables need replacement
This makes it a strong option for users thinking beyond short-term expenses.
Eco-Friendly and Reduced Waste
Sustainability is another key advantage. By eliminating frequent cartridge disposal, an Ink Tank Printer helps reduce plastic waste and packaging materials.
Environmental advantages include:
- Fewer cartridges sent to landfills
- Reduced packaging and shipping waste
- More efficient use of ink resources
For users who value eco-conscious choices, this technology aligns well with responsible printing habits.
Easy and User-Friendly Refilling
Modern refill systems are designed to be simple and clean. Most Ink Tank Printer models use spill-resistant bottles and clearly marked refill ports, making the process manageable even for beginners.
Practical benefits:
- Minimal mess during refilling
- Clear guidance from manufacturers
- Reduced risk of incorrect ink installation
Drawbacks of Ink Tank Printers
While the advantages are compelling, it is equally important to understand the limitations before choosing an Ink Tank Printer.
Higher Initial Cost
One common drawback is the higher upfront price. Compared to basic cartridge printers, an Ink Tank Printer usually costs more at the time of purchase.
This may be a concern for:
- Users with tight initial budgets
- People who print only occasionally
For light users, the long-term savings may not justify the higher entry cost.
Bulkier Physical Size
Because of the built-in ink tanks, many models have a larger footprint. An Ink Tank Printer may take up more desk or shelf space than compact cartridge printers.
Considerations include:
- Limited workspace availability
- Portability concerns
- Placement in small home offices
Potential Mess During Refilling
Although refilling systems have improved, there is still some risk of spills if refilling is done carelessly. Unlike cartridges, bottled ink requires more attention.
Possible issues:
- Ink stains if mishandled
- Need for careful refilling technique
This drawback is minor but worth noting for first-time users.
Slower Performance for Some High-Speed Needs
While efficient for volume, some Ink Tank Printer models are not designed for ultra-fast printing. Laser printers may still outperform them in speed-heavy office environments.
This matters if:
- Speed is the top priority
- Large batches must be printed quickly
Maintenance and Printhead Clogs
If an Ink Tank Printer is left unused for long periods, dried ink can clog the printhead. Regular use helps prevent this, but occasional maintenance may be required.
Maintenance considerations:
- Periodic cleaning cycles
- Best suited for regular printing
According to HP Tech Takes:
“Ink tank printers, also known as Smart Tank printers, allow higher ink capacity and significantly lower cost per page compared with cartridge printers.”
This reinforces the idea that these printers are optimized for frequent use rather than long idle periods.
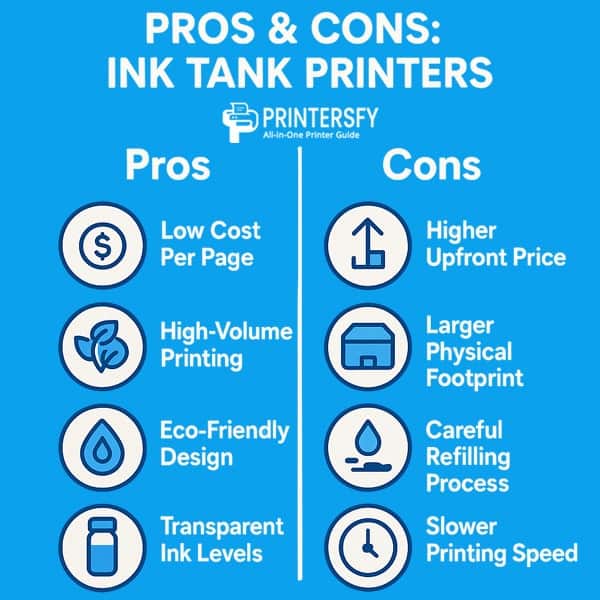
Pros & Cons: Ink Tank Printers
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Low cost per page | Higher upfront price |
| Good for high-volume prints | Larger footprint |
| Eco-friendly | Requires careful refill |
| Transparent ink levels | Not the fastest speed |
Use Cases & Who Should Consider Buying One
With a clear view of the strengths and weaknesses, the final question is whether an Ink Tank Printer fits your specific needs. This technology is not designed for everyone, but it excels in certain use cases.
Home Users and Students
For households with regular printing needs, an Ink Tank Printer offers excellent value. Students benefit from low-cost printing for assignments, notes, and study materials.
Why it works:
- Affordable long-term printing
- Fewer ink purchases
- Reliable for everyday use
Small Offices and Businesses
Small businesses often prioritize efficiency and cost control. An Ink Tank Printer supports frequent document printing without recurring cartridge expenses.
Best for:
- Invoices and reports
- Administrative paperwork
- Daily operational printing
This makes it a strong contender for the best printer technology in cost-conscious offices.
Photo Creators and Designers
While not all models are photo-focused, many Ink Tank Printer options deliver good color accuracy and consistency.
Suitable for:
- Casual photo printing
- Graphics and marketing materials
- Creative home projects
Who Should Avoid It
If you print very rarely, an Ink Tank Printer may not be ideal. Occasional users might face ink drying issues and may not recover the higher initial cost.
Not ideal for:
- Very light or infrequent printing
- Users prioritizing compact size over efficiency
Ink Tank Printers vs Other Liquid Ink Printer Technologies
After exploring how refillable ink systems work and who they are best suited for, it helps to place them in context with other liquid ink printer technologies. While these printers all use liquid ink, their design, purpose, and ideal users can differ significantly.
Ink Tank Printers vs Traditional Inkjet Printers
At first glance, ink tank–based models and traditional inkjet printers may seem similar because both rely on liquid ink and inkjet technology. The main difference lies in how ink is stored and consumed.
Standard inkjet printers use small, sealed cartridges that need frequent replacement. This makes them convenient for occasional printing but costly over time. In contrast, an Ink Tank Printer uses large refillable reservoirs, allowing users to print far more pages at a lower cost per page.
Traditional inkjets are best for:
- Light or occasional printing
- Users who prioritize low upfront cost
Refillable ink models are better suited for:
- Frequent or high-volume printing
- Users focused on long-term savings
Ink Tank Printers vs Graphics Printers
Graphics printers are designed primarily for professional visual output, such as posters, banners, and detailed design work. They often use advanced color management systems and specialized inks to achieve superior color accuracy and consistency.
While an Ink Tank Printer can handle documents, charts, and casual photo printing very well, it is not intended to replace professional graphics printers. Graphics printers are typically larger, more expensive, and built for creative professionals who require precise color matching.
Key differences include:
- Graphics printers focus on color accuracy and media variety
- Refillable ink printers prioritize cost efficiency and everyday use
For general users and small offices, ink tank–based printers offer a practical balance between quality and affordability.
Ink Tank Printers vs Direct-to-Garment (DTG) Printers
Direct-to-Garment (DTG) printers are highly specialized machines used for printing designs directly onto fabric, such as T-shirts and textiles. Although they also use liquid ink, the similarities largely end there.
DTG printers require:
- Textile-specific inks
- Pre-treatment processes
- Dedicated production workflows
An Ink Tank Printer is not designed for fabric printing and should not be considered an alternative to DTG technology. DTG printers are aimed at apparel businesses, while refillable ink printers focus on paper-based printing tasks.
Each liquid ink printer technology serves a different purpose. Traditional inkjets suit occasional users, graphics printers serve creative professionals, and DTG printers meet textile production needs. An Ink Tank Printer, however, stands out as a versatile and cost-efficient option for users who print regularly and want predictable long-term expenses.
Conclusion
An Ink Tank Printer is designed for users who want efficient, cost-effective, and reliable printing without the constant hassle of replacing ink cartridges. By using large refillable ink reservoirs, this printer type delivers a continuous ink supply that supports high-volume printing at a much lower cost per page. Instead of focusing on short-term convenience, it prioritizes long-term savings and consistent output.
From a technical perspective, the system works by storing ink in built-in tanks and feeding it directly to the printhead through a controlled delivery mechanism. This approach reduces interruptions, improves efficiency during long print jobs, and makes ink usage easier to monitor. Over time, these advantages translate into better value, especially for users who print regularly.
The benefits are clear: lower running costs, reduced plastic waste, and reliable performance for everyday documents, schoolwork, office reports, and even occasional photos. At the same time, it’s important to consider the limitations, such as higher upfront cost, larger physical size, and the need for regular use to avoid maintenance issues.
So who should choose this technology? Students, home users, small offices, and anyone focused on high-volume printing savings will gain the most value. On the other hand, very light or infrequent users may still be better served by simpler alternatives.
If you print often and want predictable expenses over time, an Ink Tank Printer is a smart long-term investment. Before buying, consider your monthly print volume, available space, and how regularly the printer will be used—these factors will help you choose the model that fits your needs best.
FAQs About Ink Tank Printer
What is an ink tank printer?
It is a printer that uses large refillable ink tanks instead of small cartridges, allowing users to print more pages at a lower cost per page.
What is the difference between an inkjet and an ink tank?
Traditional inkjet printers use cartridges, while ink tank models use refillable reservoirs. The main difference is running cost and print volume capacity.
Which is better, a laser or ink tank printer?
Laser printers are faster and better for text-heavy office work, while ink tank models are ideal for frequent color and document printing with lower long-term costs.
Does an ink tank printer break if not used for a long time?
It usually won’t break, but infrequent use may cause printhead clogs. Regular printing helps keep the system in good condition.
Should I buy an inkjet or ink tank printer?
Choose an inkjet for occasional use and low upfront cost. Choose an ink tank printer if you print regularly and want long-term savings.




